2.2.2 Parthenolide
Biological Source It is
obtained from the leaves of Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Schultz-Bip, belonging
to family Asteraceae. It is commonly known as feverfew and has
been employed for centuries as an effective febrifuge (antipyretic) which
perhaps suggested the original nomenclature.
It is also obtained from Chrysanthemum
parthenium (L.) Bernh. Family Compositae; and
Magnolia grandiflora (L.)
family Magnoliaceae.
Geographical Source The
plant M. grandiflora is a native of North America and also cultivated in
Indian gardens.
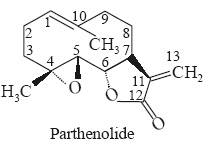
Chemical Structure Parthenolide
is a sesquiterpenoid lactone having the following structure with the
chemical name 4,5α-epoxy-6 β-hydroxy germacra-1 (10), 11(13)-dien-12-oic acid γ-lactone.
It has an additional epoxide
bridge between 4-and 5α-positions.
Uses
1. It is found to act as a serotonin
antagonist thereby causing an inhibition of the release of serotonin from
blood platelets.
2. Based on the findings conducted by an
elaborated double blind placebo-controlled clinical trials have established
that the drug is significantly effective in the prophylaxis of migraine by
reducing considerably the severity as well as the frequency of the pain due to
headache.
3. A normal dose of 125 mg per day of good
quality dried leaves either in the form of tablets or capsules are used in the therapeutic
practice as an antipyretic or febrifuge.
Source:Pharmacognosy And Pharmacobiotechnology By Ashutosh Kar
Source:Pharmacognosy And Pharmacobiotechnology By Ashutosh Kar






















0 Comment:
Post a Comment