2.1.1 Camphor
Synonyms Gum camphor;
Japan camphor; Formosa camphor. Laurel camphor.
Biological Source It
occurs in all parts of the camphor tree, Cinnamonum camphora. T. Nees
& Ebermeier, belonging to family Lauraceae.
Geographical Source The
word camphora is derived from the Arabic Kafur, meaning chalk.
The camphor tree, which is a huge evergreen plant, is found to be
indigenous to Japan, China and Taiwan. It has also been naturalized
specifically in the Mediterranean region eg; Algeria, Tunsia, Libya, Egypt,
Italy and Greece. Besides it is grown in South Africa, Ceylon, Brazil, Jamaica,
Florida and California. History reveals that Borneo camphor (from Borneol)
arrived in Arabia in the sixth century and in Europe in the twelth century.
Earlier, the worlds 80% supply of natural camphor was provided by Taiwan
(Formosa) alone and the rest 20% by Japan and Southern China. Soonafter the second
World War (1945) the commercial production of synthetic camphor has more
or less catered for the ever increasing demand of camphor in the world
market.
Preparation It is
prepared from the chipped wood by subjecting it to steam distillation and subsequently
collecting the distillate in specifically designed chambers where camphor will
solidify on its miner walls upon colling and may be collected later on from the
bottom of the chamber. The crude solidified camphor is purified by mixing it
with a suitable proportion of soda lime, sand and charcoal; and subjecting the
mass to sublimation at controlled temperature when pure crystals of camphor
would be collected as a sublimate. It is finally compressed into either small cubes
or thin plates, wrapped and exported.
Camphor from Volatile Oils It
may be prepared from volatile oils by two simple methods, namely:
Methods-I In case, the oil
contains a substantially large proportion of camphor, it may be
separated
by deep freezing or sudden
chilling; and if the camphor content in oil is not so much it is mostly fractionated
and the camphor containing fraction is chilled to recover camphor.
Method-II Camphor may be
recovered from volatile oils by the instant production of insoluble complexes
with strong mineral acids eg; sulphuric acid 80% (30N).
Synthetic Camphor (or
Borneol Camphor) The camphor is obtained commercially from α-pinene
present in the turpentine oil through several steps sequentially e.g.,
treatment with HCl, isomerization, treatment with KOH and finally oxidation
with HNO3 as given below:
Colour : Translucent
mass with crystalline fraction
Odour : Characteristic
odour
Optical Activity :
Natural camphor = Dextro rotatory (+ 41o to 43o)
Synthetic camphor = Racemic mixture;
Solubility : Soluble in
water (1:600)
Chemical Structure Camphor is
a bycyclic terpenoid ketone as given below:
In the presence of platinum
black it undergoes hydrogen at ambient temperature giving rise to isoborneol
as the major product and traces of borneol.



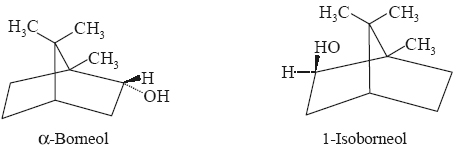






















0 Comment:
Post a Comment